dijkstra algorithm and its implementation
wiki : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm
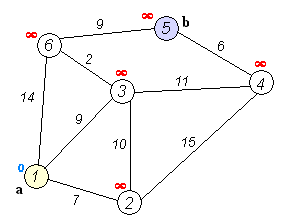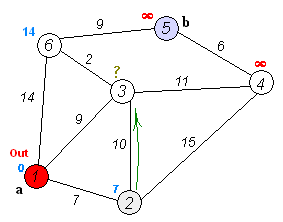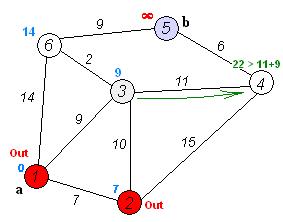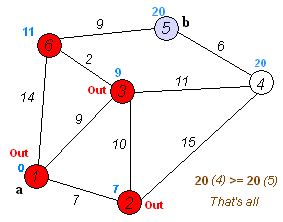
특정 두 노드 간의 최단 거리를 구하는 데 사용함.
distance 가 양수 값을 가지는 경우에만 적용.
알고리즘
아래 알고리즘에서 u := Extract_Min(Q)는 점의 집합 Q에서 가장 작은 d[u]값을 찾은 다음 그 점 u를 Q에서 제거한 후 반환하는 함수를 가리킨다.
function Dijkstra(G, w, s)
for each vertex v in V[G] // 초기화
d[v] := infinity
previous[v] := undefined
d[s] := 0
S := empty set
Q := set of all vertices
while Q is not an empty set // 알고리즘의 실행
u := Extract_Min(Q)
S := S union {u}
for each edge (u,v) outgoing from u
if d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v) // (u,v)의 경감
d[v] := d[u] + w(u,v)
previous[v] := u //경로 추적할 때 쓰임
만약 모든 v에 대해서가 아니라 특정한 s에서 t까지의 최단 거리만을 알고 싶다면 9번째 행에서 u = t일 때 종료하면 된다.
s에서 t까지의 최단 경로는 다음과 같이 얻을 수 있다.
S := empty sequence
u := t
while defined u
insert u to the beginning of S
u := previous[u]
이제 S는 s에서 t까지의 최단경로 상에 있는 점들의 목록이 된다.
Extract_Min() 를 구현하는 방법 ?
소스 코드
class Line { public:
Line(int t, int c) : to(t), cost(c) {}
int to, cost;
bool operator <(const Line& l) const { return to < l.to; }
};
int n;
bool visit[10000];
vector<Line> line[10000];
class Node { public:
Node(int i, int c) : index(i), cost(c) {}
int index, cost;
bool operator >(const Node& l) const {
return cost > l.cost;
}
};
void dijkstra() {
int i;
memset(visit, 0, sizeof(bool) * 10000);
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, greater<Node> > Q;
Q.push(Node(0, 0));
int solution = 0;
while (!Q.empty()) {
Node node = Q.top();
Q.pop();
if (visit[node.index]) continue;
if (node.index == n-1) {
solution = node.cost;
break;
}
visit[node.index] = true;
vector<Line>::const_iterator it = line[node.index].begin();
for (; it != line[node.index].end(); it++) {
if (!visit[it->to]) {
Q.push(Node(it->to, node.cost + it->cost));
}
}
}
cout << solution << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // release
line[i].clear();
}
}
Written on August 20, 2015